Rotary speed sensors are tools, for measuring how fast something rotates. They are used in a wide range of fields such as mechanical engineering, vehicle dynamics and hydraulic systems. These sensors, which are a type of position sensors, have a role in overseeing and regulating the speed of various machinery to ensure efficiency and safety in different industries.
This article dives into the working principles of rotary speed sensors, their different types and their importance. Additionally it delves into the applications of these sensors across industries while discussing important specifications and future trends. This provides insights, into why these sensors are crucial in today’s technological landscape.
Working Principle of Rotary Speed Sensors
Rotary speed sensors play a role, in gauging speed across different contexts relying on distinct underlying principles tailored to specific environmental settings and measurement needs. This overview delves into the mechanisms of these sensors encompassing Hall effect sensors, LC wireless sensors, magnetoresistive sensors and other variants.
Hall-Effect Sensors:
The Hall principle is used to leverage the Lorentz force, which causes moving charge carriers to change direction in a field. This process results in the creation of a Hall voltage indicating variations, in the field.
By detecting movements of objects such as gears the sensors can identify shifts in flux and produce a square wave voltage output that mirrors these alterations.
Differential Hall sensors as a variation gauge the distinction, between two Hall elements making them well suited for challenging environments and gear mechanisms with irregular paths.
LC Wireless Sensors:
Include two matching LC resonant circuits, where the coil, on the moving section aligns co with the reader coil when rotating. This alignment enhances interaction resulting in peak signal strength at the reader LC circuit.
The frequency of the reader signal is directly tied to the velocity offering an approach, to detecting rotation speed.
Magnetoresistive and Inductive Sensors:
- Magnetoresistive Sensors: Use the resistance of the sensor based on the strength and orientation of a field. These sensors work well for tasks that need tracking of how something is rotating.
- Inductive Sensors: Integrate an oscillator circuit that produces a radio field. When a metal target is introduced it creates currents that modify the amplitude of the oscillator circuit. This shift, in amplitude serves as an indication of the speed.
- Variable Reluctance Sensors: Generate a charge by placing a surface nearby without the need, for an external power supply. These self-powered sensors are perfect, for speed sensing applications.
Moreover optical sensors and TMR (tunnel Magnetoresistive) sensors provide approaches, to measuring speed. Optical sensors use reflection from a rotating object while TMR sensors detect resistance changes caused by a rotating magnetic field. Both sensor types offer benefits serving industries such, as automotive and aerospace showcasing the versatility and significance of rotary speed sensors in today’s tech landscape.
Types of Rotary Speed Sensors
Different types of rotary speed sensors are classified according to how they work and their design, serving purposes, in industries and automotive settings. The main varieties consist of:
Magneto-Resistive Rotational Speed Sensors:
- Key Features: Utilize the resistance changes in sensing elements due to the magnetic field’s direction and magnitude.
- Applications: Ideal for precise measurements of rotational speed in environments where accuracy is paramount.
Inductive Rotational Speed Sensors:
- Key Features: Operate on the principle of inducing eddy currents in a metal target, affecting an oscillator circuit’s amplitude.
- Applications: Suitable for detecting metal targets in motion, commonly used in automotive and industrial machinery for speed measurement.
Hall Effect Rotational Speed Sensors:
- Key Features: Rely on the Hall effect, where a voltage is developed across a conductor when it is exposed to a magnetic field perpendicular to the direction of the electric current.
- Applications: Extensively used in proximity rotational speed recording on gears with small modules, offering high resolution in a wide range of applications, including industrial trucks, construction machines, and agricultural equipment.
Several manufacturers have specialized in developing rotary speed sensors designed to withstand challenging conditions:
- RHEINTACHO: Focuses on Hall-effect sensors, ensuring their products can endure high pressure, temperature fluctuations, electromagnetic disturbances, and aggressive media.
- Philips Semiconductors: Offers the KMI15/16 rotational speed sensors, providing cost-effective solutions for automotive and industrial applications.
- Variohm: Sources magnetic speed sensors from Phoenix America, catering to diverse measurement needs.
Rotary speed sensors are valuable, in situations where measuring without contact’s crucial particularly in hard to reach locations or challenging conditions. Selecting the sensor type depends on factors like precision needs, operating environment and the characteristics of the target being monitored. Brands such as RHEINTACHO Philips Semiconductors and Variohm have customized their products to cater to a range of requirements guaranteeing a rotary speed sensor solution, for almost any situation.
Importance of Rotary Speed Sensors
Rotary speed sensors are crucial, in today’s automotive settings playing a role, in maintaining the safety, effectiveness and dependability of machinery across different situations. Their significance stems from aspects;
Contactless Measurement Capabilities:
- Enables speed and rotation monitoring in locations that are either inaccessible or where traditional contact methods would be impractical.
- Essential for applications where physical contact with the rotating element could introduce friction or contamination, affecting performance.
Durability and Resistance:
- Engineered to withstand extreme environmental conditions, including exposure to hydraulic oil, salt, alkaline solutions, acid, and temperature variations from -40 °C to +160 °C.
- Their robustness makes them suitable for harsh industrial environments, where they can reliably function without degradation over time.
Versatility and Application Range:
- With a measurement frequency range from 0 Hz to 30,000 Hz, rotary speed sensors can accurately monitor a wide array of machine components.
- Their utility spans across various sectors, including but not limited to, industrial trucks, construction machines, agricultural machinery, rail vehicles, wind power plants, and motorsport vehicles.
- Particularly effective for gear rotation monitoring, requiring directional installation to ensure optimal performance.
Rotary speed sensors play a role, in monitoring and controlling systems under conditions while ensuring accuracy and reliability. Companies like RHEINTACHO excel in creating sensors that can withstand pressures temperature changes, electromagnetic interference and other harsh environments showcasing the engineering and innovation required for these crucial devices.
In essence rotary speed sensors are essential for upholding the efficiency and functionality of machinery, in industries. Their durability and ability to measure precisely without contact make them a fundamental technology driving advancements in automotive systems.
Applications in Industry
Rotary speed sensors are widely used in a variety of industries, for monitoring rotational speeds and ensuring machinery operates optimally thanks, to their precision and reliability. These sensors can be integrated into vehicles and machinery highlighting their importance in today’s processes.
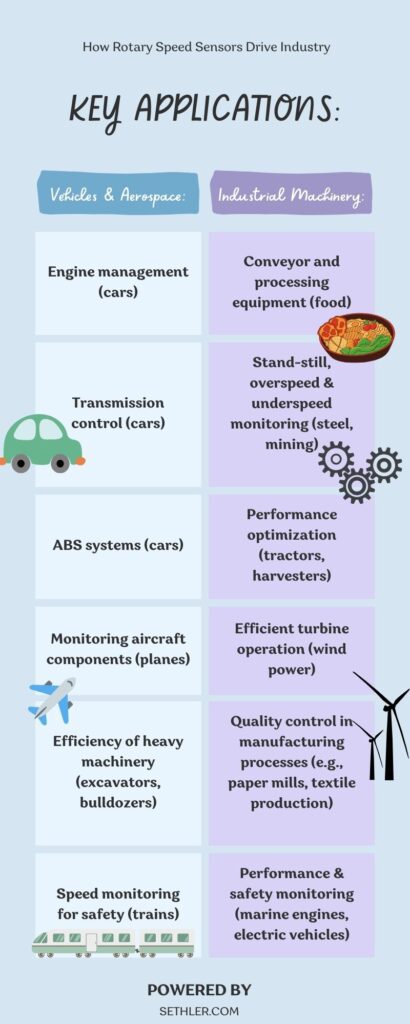
Vehicle and Aerospace Applications:
- Automotive: Engine management, transmission control, and ABS systems.
- Aerospace: Monitoring and controlling the speed of aircraft components.
- Off-Highway & Construction: Ensuring the efficiency of heavy machinery like excavators and bulldozers.
- Railway: Speed monitoring for safety and performance optimization.
- Military Vehicles: Critical for navigation and operational effectiveness.
Industrial Machinery and Applications:
- Food Industry: Speed control of conveyors and processing equipment.
- Steel and Mining: Monitoring equipment for standstill, over speed, and under speed conditions.
- Agriculture: Optimizing the performance of tractors, harvesters, and other farming machinery.
- Wind Power Plants: Ensuring the efficient operation of turbines.
- Marine Engines and Electric Vehicles: Monitoring rotational speed for performance and safety.
Custom Solutions and Standard Products:
- RHEINTACHO and Philips Semiconductors, along with companies provide a variety of rotary speed sensors designed to meet specific industrial requirements. They offer options with casings, designs and interfaces as well, as customized solutions that can be developed promptly and affordably.
- KMI15/16 sensors, designed primarily for automotive applications, are also adaptable for various industrial uses, demonstrating the flexibility of rotary speed sensors in meeting diverse measurement requirements.
The use of rotary speed sensors, in these settings enables supervision and management of equipment and vehicles enhancing safety, effectiveness and dependability. Manufacturers such as RHEINTACHO provide a range of off the shelf options and tailored solutions to ensure the availability of speed sensors for a range of situations showcasing the versatility and significance of these devices, in industrial and automotive fields.
Key Specifications and Selection Criteria
Recognizing the importance of rotary speed sensors, in a wide range of applications it is crucial to explore the essential specifications and selection criteria that influence their use and integration. These requirements not assess the appropriateness of a sensor for an application but also showcase the progress and evolution, in sensor technology. Here’s an overview of the factors to consider;
Key Specifications:
- Measurement Range: The rotary speed sensor can accurately measure a variety of speeds typically indicated in revolutions, per minute (RPM) for speed sensors and inches per minute, for linear speed sensors.
- Accuracy: The accuracy of the sensors measurements plays a role, in situations requiring speed regulation. It is essential for ensuring performance, in applications.
- Resolution: The smallest change in speed that the sensor can detect. Higher resolution allows for finer speed control and monitoring.
- Output Type: The format in which the sensor communicates its measurements, whether digital (e.g., frequency, pulse width modulation) or analog (e.g., voltage, current).
- Environmental Resistance: The ability of the sensor to withstand harsh conditions, including high temperatures, moisture, and electromagnetic interference. This is particularly important for sensors used in industrial and automotive applications.
Selection Criteria:
- Application Requirements: Consider the specific needs of the application, including the range of speeds to be measured, the required precision, and environmental conditions. For example, high-speed applications may require sensors with a high maximum speed rating and low latency.
- Sensor Type: Choose between different types of rotary speed sensors based on the application’s requirements. Options include magnetic, optical, and Hall-effect sensors, each with its unique advantages.
- Installation and Integration: Evaluate the ease of installation and integration with existing systems. This includes considering the sensor’s physical dimensions, mounting options, and connectivity options (e.g., wireless, Bluetooth, USB).
- Cost-effectiveness: While quality and performance are paramount, the cost-effectiveness of the solution must also be considered. This includes both the initial purchase cost and the long-term operational costs.
By thoroughly evaluating these specifications and criteria, individuals and organizations can select the right rotary speed sensor that meets their specific needs and contributes to efficient and safe operation.
Innovations and Future Trends
The market, for rotary speed sensors is poised for expansion and change fueled by a mix of technological advancements and shifting industry needs. Important observations, about this market include;
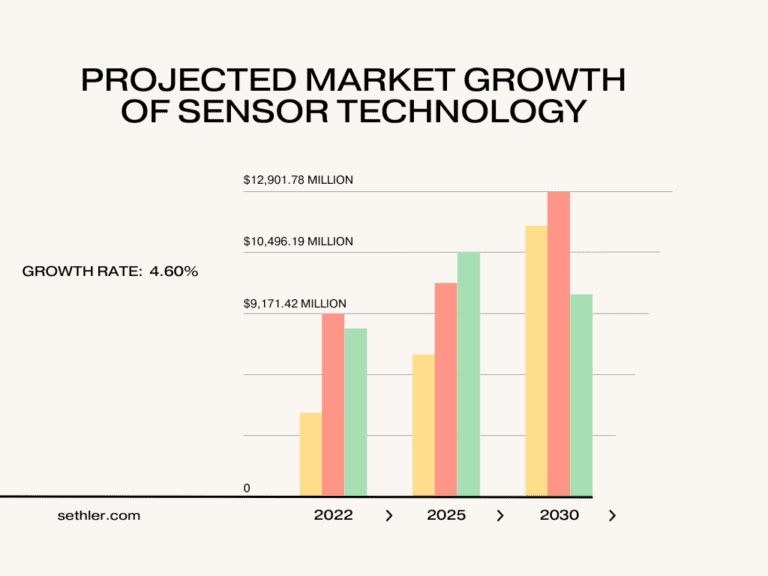
Projected Market Growth:
The wider market, for speed sensors including rotary speed sensors was valued at $9,171.42 million in 2022. Is projected to reach over $12,901.78 million by 2030 with a growth rate of 4.60%, during the forecasted period.
Market Drivers and Opportunities:
The market is experiencing growth due, to progress and increased awareness well as partnerships and supportive regulations. The use of speed sensors with systems improvements in sensor tech and increased automation in sectors are key factors driving this growth. New opportunities are arising from innovations like vehicles, self-driving cars and Industry 4.0. Emphasizing sustainability and energy efficient solutions is also crucial, in this context.
Innovations in Sensor Technology:
- Allegro MicroSystems is at the forefront with its GMR Wheel Speed Sensors, offering higher accuracy and lower jitter thanks to advancements in GMR Technology.
- The introduction of high-resolution wheel-speed sensors (A19360) by Allegro MicroSystems, generating four times the resolution of standard sensors, marks a leap in sensor capabilities.
- Infineons range of magnetic speed sensors incorporating GMR based and Hall-effect technology demonstrates the industry’s shift, towards enhanced, dependable and adaptable sensor solutions. Noteworthy products such as the TLE4941plusC magnetic speed sensor and the TLE4953C automatic transmission speed sensor signify the progress in technology.
Future trends in rotary speed sensor technology are shaping up to revolutionize the way rotational speeds are monitored and controlled. Key trends include:
Integration with Advanced Technologies:
The use of Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), and Edge Computing in rotary speed sensors enables smarter, more efficient monitoring and control systems.
Wearable Sensors and Energy Harvesting technologies are being explored for their potential in enhancing sensor functionality and efficiency.
Wireless Connectivity and MEMS:
Wireless connections are more prevalent now making it easier to transfer data and monitor devices from a distance. By integrating electro mechanical systems (MEMS) and fiber optics into rotational speed sensors their accuracy and dependability have significantly improved, allowing them to be used in a wider range of situations.
These advancements and shifts highlight the changing landscape of rotary speed sensors in the market. With progress these sensors are anticipated to broaden their applications and functions emphasizing their significance, in diverse industries.
Conclusion
Throughout our exploration of rotary speed sensors we have delved into understanding their operational principles, various types and significant roles, across different industries. The conversation not shed light on the functions these sensors serve in measuring and controlling rotational speeds but also emphasized their vital role in ensuring efficiency, safety and reliability in a wide range of systems and applications. From the basics of their design to the cutting edge innovations shaping their future rotary speed sensors showcase the blend of technology and practical use.
Looking ahead the trajectory of rotary speed sensors shows a path towards technological advancement and integration driven by increasing demands for precision, durability and versatility. The anticipated progress and broader application possibilities call for exploration and innovation presenting opportunities for industries spanning from automotive to aerospace and beyond. Thus embracing the advancements in sensor technology will be key to unlocking the potential of these essential devices solidifying their pivotal position, in modern industry and technology landscape.

